THE DARK FORCE OF THE SPOTS
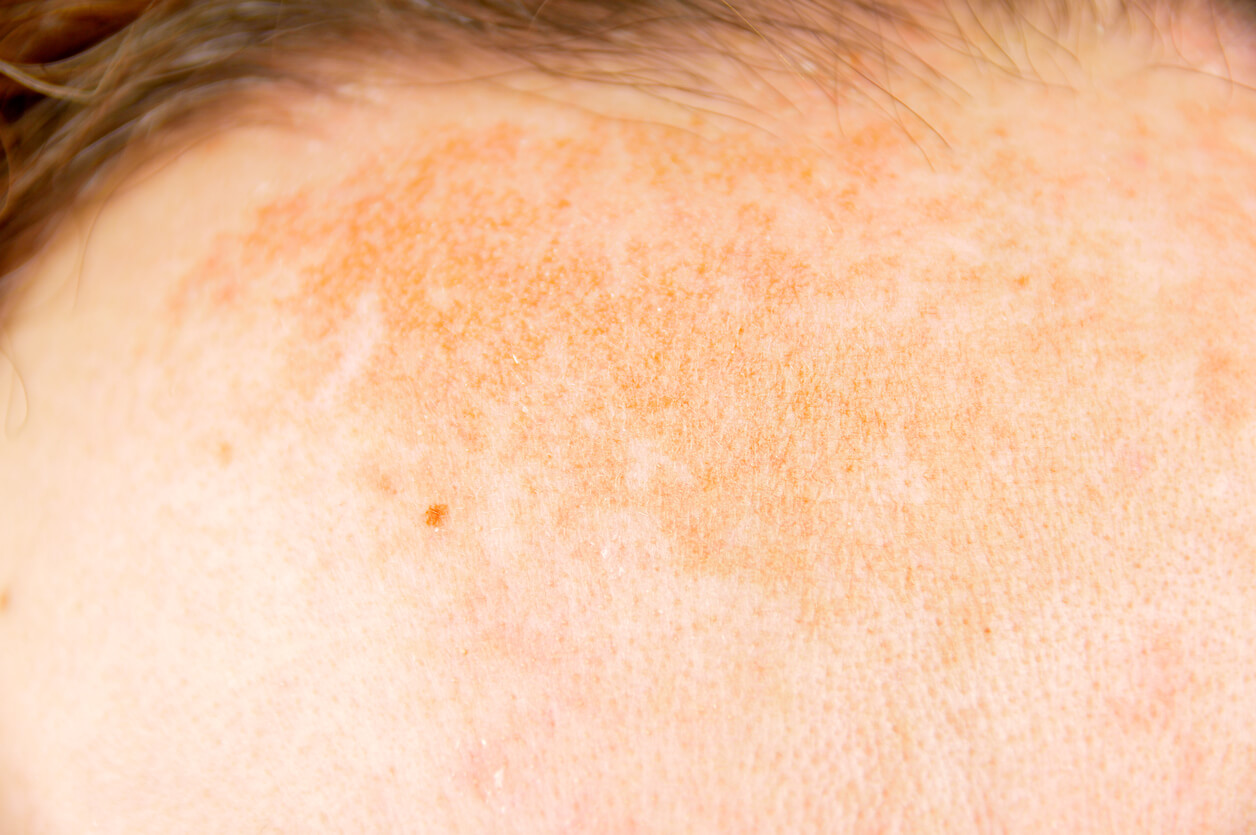
Do you remember the 80s? What about all those times you laid out in the sun baby oil and aluminum foil in tow? All of those years of fun in the sun came with consequences that no one really seemed alarmed about during the age of Jane Fonda and teased bangs. Now as you’ve begun to age, you may notice dark spots that have popped up all over your skin. Known as hyperpigmentation, these dark spots are really your bodies way of protecting you from the sun and other environmental damage. Even so, there isn’t anyone around that considers dark spots a good thing. Luckily, there are ways you can battle the appearance of dark spots on the face. In order to understand how to brighten up skin tone and get rid of dark spots, we have to understand why we become hyperpigmented and what we can do to erase the appearance of these unfortunate dark spots.
HOW A TIGER EARNS ITS STRIPES
Most commonly affecting lighter shades of skin, hyperpigmentation has been on the rise in recent years in all skin colors. To understand why let’s take a closer look at how your skin gains its color. There are many factors that determine the color of your complexion. A few of these factors that play a big role are the number of melanocytes, the amount of melanin produced, and the type of melanin within your body. Melanocytes are special skin cells that produce melanin, a biological pigment found in the hair, skin, and nails. They are usually distributed evenly throughout the skin with more being found in those with darker complexions. Melanin production actually determines how fair or dark a person is. For example, the complexion difference between Caucasian and Asians are primarily dependent on the amount of melanin produced. The type of melanin produced also plays a role. There are two types of melanin: pheomelanin and eumelanin. The more eumelanin that’s produced, the darker your complexion is. Pheomelanin can be converted to eumelanin by a special enzyme in melanocytes. People with very fair skin frequently have a genetic polymorphism in the gene encoding the enzyme which prevents the conversion between pheomelanin and eumelanin leading to a lighter color of hair, eyes, and skin. In skincare, most creams to cure hyperpigmentation focus on suppressing the melanocytes ability to produce excess melanin. But what if there was a way to inhibit the melanin production or kill all the melanocyte all together, then there may be a way to forego hyperpigmentation all together? Though it sounds like a good idea, the melanocytes distributed throughout your body are actually vital for other organs as well. In your iris, for example, they work to help you focus and prohibit eye damage by serving as a screen to filter out the bad rays. In the hair in your ears, the melanocytes work to aid auditory processing.
WHEN PIGMENT IS DISTURBED
You’ve probably heard of Leukoderma, or Vitiligo, which is a disease that causes the skin to have white spots usually in a patch-like form over the skin, though it can also affect the eyes and hair. It happens as the result of an autoimmune disease that causes the body to destroy its own melanocytes. Treatment can help but the disease is lifelong. There are also cases when there is not enough pigment found in a person’s body. Albinism, which is marked by a characteristic fair skin color with light eyes and white hair is caused by not having enough fully pigmented melanosomes. It occurs when a mutation in the tyrosinase impairs the production of melanin. In those with albinism, there’s a noticeable lack of pigment.
Another way that pigment can be disturbed is through sun damage. Damage from sun exposure is one of the leading causes of hyperpigmentation in fair-skinned people. Over time, as you lay out in the sun without sunscreen, your body will produce patches of over-produced melanin that leaves behind blotchy areas as you age. Most damage is done to the outer layer of skin, called the epidermis, and there is treatment available that can help lighten the skin and improve the appearance of dark spots.
As you begin to think about treatments that help lighten the skin, it’s important to know that there is a limit to how fair your skin can go. Think about Michael Jackson for a second. An autopsy of the singer showed that he did indeed have Vitiligo, the disease that causes the skin to lose its melanin and have a patchwork appearance. To help with his disease, Jackson used skin bleaching with monobenzyl ether of hydroquinone to give his skin a more even appearance. This caused a lot of questions to arise about the singer’s strikingly fair complexion during the 80s.
THE MELANIN-KERATINOCYTE TRANSFER PROCESS
Once melanin is formed in the melanocytes of your skin found in the dermis layer, melanin is then transferred to keratinocytes. Each melanocyte is in contact with as many as 36 keratinocytes, which is one reason hyperpigmentation appears as spots or patches.
[insert image of transfer process with explanation]
The moral of the story? There are multiple targets in the whole process of melanin production that each plays an important and active role in creating, healing and reproducing the skin pigment. To brighten up the skin or get rid of the spots, you must be actively aware of these many elements of the process and how they work together so that you can properly treat your skin.
- Targeting tyrosinase the enzyme catalyzing melanin synthesis. Tyrosinase is an oxidase that helps regulate the production of melanin. Problems with this can cause too little or too much melanin to be made.
- Formation of melanosome. Little sites of melanin production, they are the location where the synthesis, storage, and transport of melanin pigments occur.
- Transport of melanosome. The process of moving melanin from the melanocyte to the keratinocyte where it can be released from the body.
FIGHTING BACK AGAINST DARK SPOTS ON THE FACE
Now that you understand the complex process that occurs when your body is protecting your skin from the elements, you can understand why there must be targeted therapy to treat the problem. Thankfully, there are many brightening ingredients used in skincare products that help to reduce the appearance of dark spots on your skin. You must always make it a priority to be a well-researched consumer, however, because certain skin lightening products are still being studied and others are banned from use. Here are the products you need to know about so that you can treat your hyperpigmentation properly.
- A topical agent placed on the skin to bleach or brighten dark spots. It works by competitively inhibiting active tyrosinase, disrupting the formation of melanosome, consuming glutathione and killing melanocytes. Prescription grade contains 4 percent hydroquinone and it’s the star ingredient in Obagi skincare. Recently, however, the FDA removed it from the safe product list because it is potentially carcinogenic. It is also banned in the European Union (EU).
- A natural product which can be hydrolyzed in the body and give rise to hydroquinone. It’s also banned in EU and Japan due to its potential carcinogenic nature.
- Kojic acid. A by-product of rice fermentation when sake is created, it works by inhibiting tyrosinase. It does have antioxidant properties.
- Azelaic acid. Made from rye, barley, and wheat, it targets tyrosinase to stop cell production and can be cell toxic.
- L-ascorbic acid. Known for its ability to help with hyperpigmentation by inhibiting tyrosinase, vitamin C is being constantly researched. Current research is studying the best way to apply it to the skin so that it absorbs and works correctly. A main ingredient in Skinceutical C E F serum.
- A super antioxidant that works to lighten the skin. It is also an active ingredient in the whitening shots that are popular for decreasing dark spots. Recently the FDA in the Philippines is researching if it really works and if it’s safe to use.
- The gold standard anti-aging ingredient helps to lighten dark spots by increasing epidermal cell turnover so that keratinocytes containing the pigment will quickly move up to the top and slough off.
- These help to reduce the inflammation of the skin and lighten dark spots.
- Vitamin b3 works to reduce inflammation and block the melanosomes from creating excessive melanin.
- Alpha hydroxyl acid. Works by peeling off layers of the epidermis with hyperpigmented spots. Leaving behind new fresh layers of skin.
- Sunscreen is so vital to everyday life. Try to choose one with a high SPF and definitely use it daily. Doing so can prevent dark spots from getting worse and can keep you from getting new dark spots as you age.
- Natural extracts. Turning to nature’s ingredients is always an important way to treat ailments of the skin. Licorice root, turmeric, soybeans are great ways to block melanin production and can be applied to the skin like a toner.
- Never ever use this to treat your hyperpigmentation. It was present in skincare in the 70s and worked quickly and effectively. It has since been banned because it is super toxic and can cause harm to your body if used.
Reducing hyperpigmentation is a tricky, complex process. It may take months to see results and you may find that a combination of treatments works the best for your skin. There’s one thing we know for sure, though all spots aren’t the result of sun damage, many are and you need to take steps today to prevent dark spots later.